nossos comerciais de novo
http://www.mdpi.com/2076-3921/3/2/323
O link acima abre o artigo que fizemos em excelente companhia (Buchner, I.; Medeiros, N.; Lacerda, D.S.; Normann, C.A.B.M.; Gemelli, T.; Rigon, P.; Wannmacher, C.M.D.; Henriques, J.A.P.; Dani, C.; Funchal, C.) sobre a relação entre o consumo de suco de uva e o seu efeito hepato-protetor. Experiência própria, é gostoso e funciona!

O resumão, em inglês:
Boa leitura!!
O link acima abre o artigo que fizemos em excelente companhia (Buchner, I.; Medeiros, N.; Lacerda, D.S.; Normann, C.A.B.M.; Gemelli, T.; Rigon, P.; Wannmacher, C.M.D.; Henriques, J.A.P.; Dani, C.; Funchal, C.) sobre a relação entre o consumo de suco de uva e o seu efeito hepato-protetor. Experiência própria, é gostoso e funciona!
O resumão, em inglês:
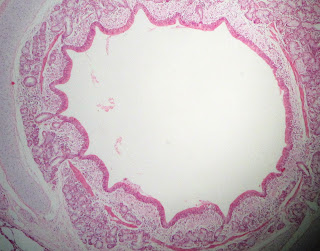
Abstract: The
objective of this study was to investigate the antioxidant and
hepatoprotective effect of the chronic use of conventional (CGJ) or
organic (OGJ) grape juice from the Bordeaux variety
grape on oxidative stress and cytoarchitecture in the liver of rats
supplemented with a high-fat diet (HFD) for three months. The results
demonstrated that HFD induced an increase in thiobarbituric
acid-reactive substances (TBARS), catalase (CAT) activity and
2′,7′-dihydrodichlorofluorescein (DCFH) oxidation and a decrease in
sulfhydryl content and superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione
peroxidase (GPx) activities. HFD also induced hepatocellular
degeneration and steatosis. These alterations were prevented by CGJ and
OGJ, where OGJ was more effective. Therefore, it was concluded that HFD
induced oxidative stress and liver damage and that the chronic use of
grape juice was able to prevent these alterations.
Keywords: liver; antioxidants; grapes; high-fat diet; free radicals
Boa leitura!!

Comentários
Postar um comentário